L o a d i n g . . . Hair Mistakes |
Exploring the Formation of Business Entities: A Comprehensive Guide
Starting a business is an exciting venture, but one of the critical decisions entrepreneurs must make is choosing the right business entity. Each type of business entity comes with its own set of advantages, disadvantages, and legal considerations.
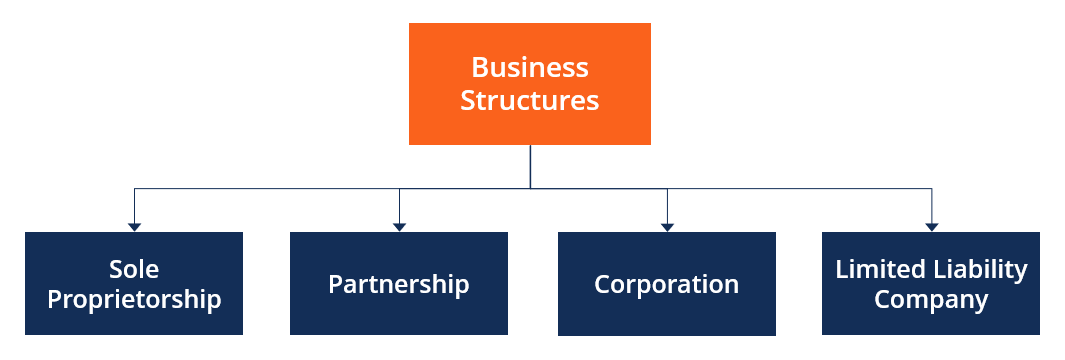
In this guide, we’ll explore the process and legal considerations involved in forming different types of business entities, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs).
Sole Proprietorships
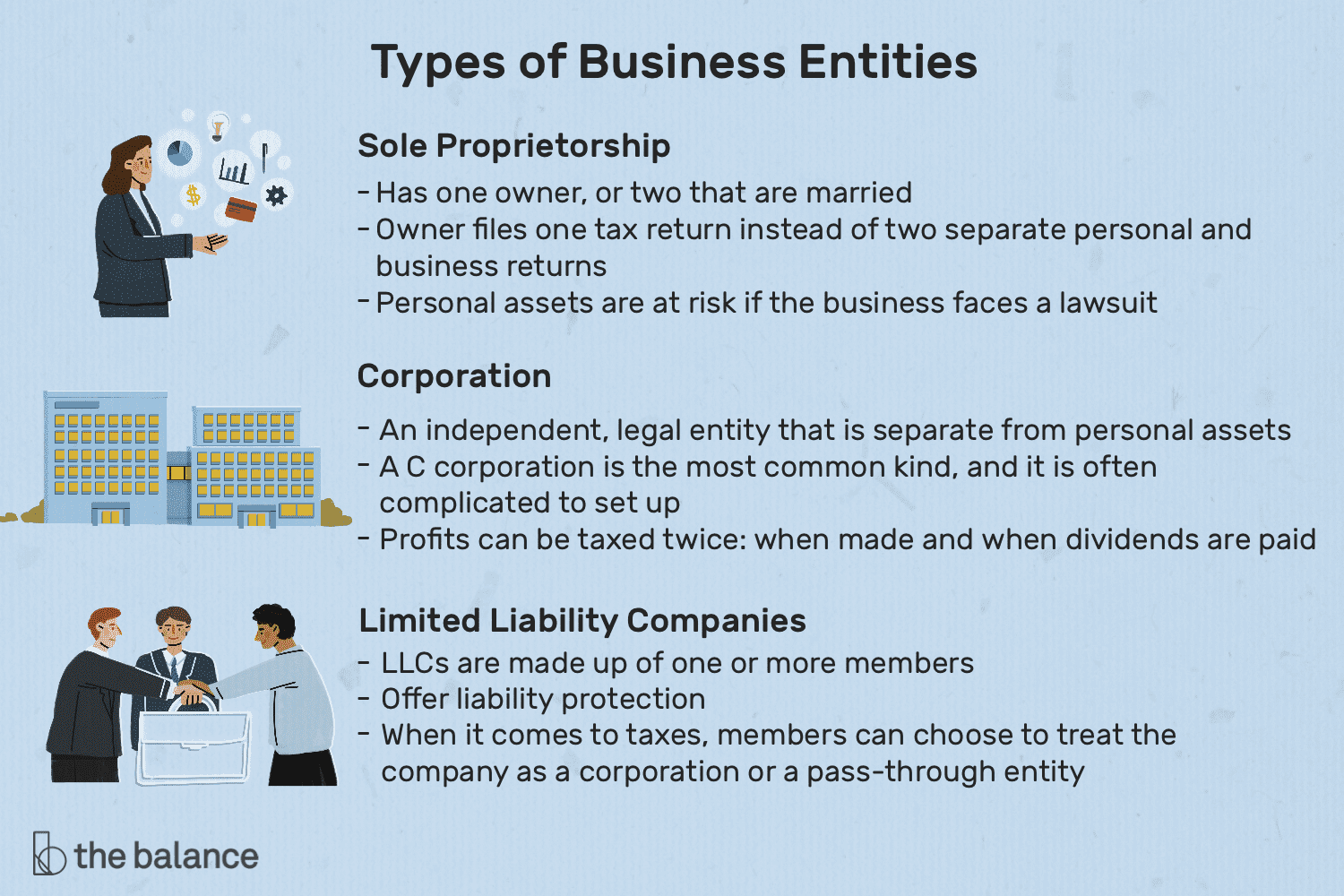
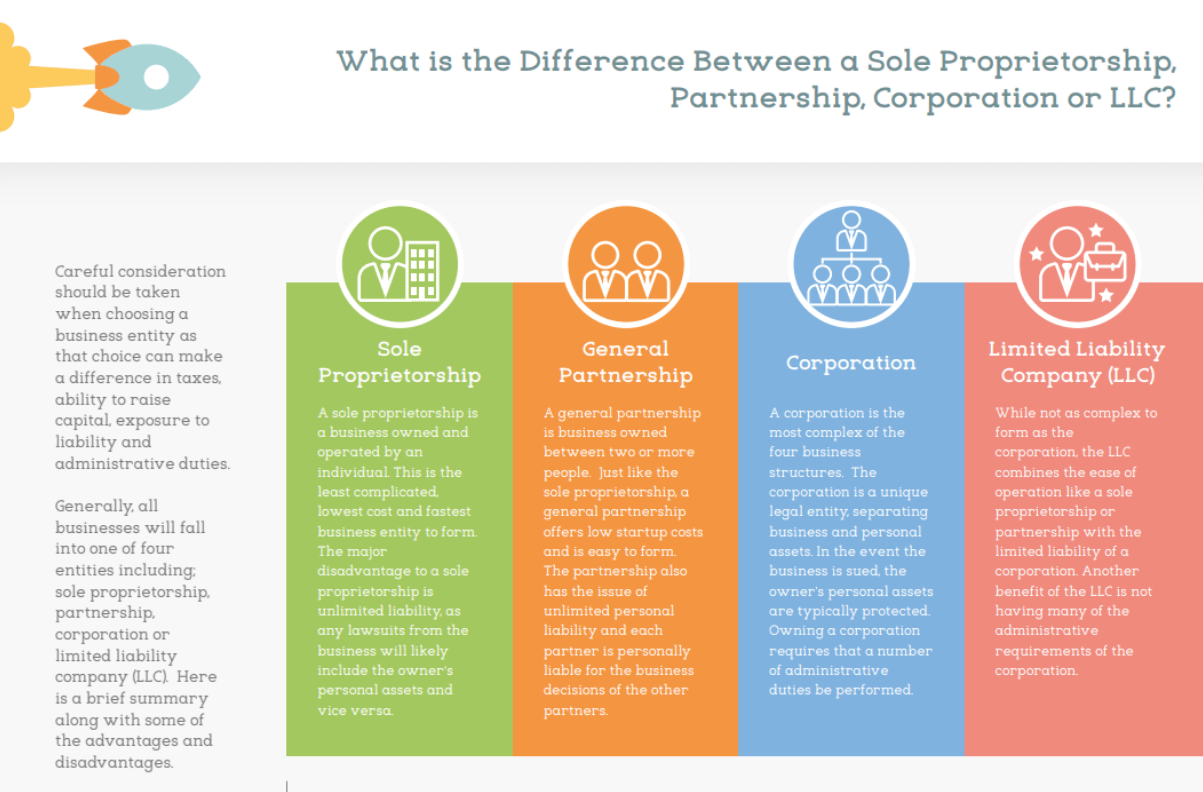
A sole proprietorship stands as the most straightforward form of business entity, owned and operated by a single individual.
Let’s delve deeper into the various aspects of forming and operating a sole proprietorship:
Process: Forming a sole proprietorship is a relatively uncomplicated procedure that does not necessitate formal registration with the state. The business owner can initiate operations under their legal name or opt for a fictitious business name, often referred to as a «Doing Business As» (DBA) name. This DBA name allows the proprietor to operate under a different business identity, providing a level of branding and professionalism without the need for formal entity formation.
Advantages: Sole proprietorships offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for many entrepreneurs:
- Ease of Formation: Establishing a sole proprietorship is hassle-free and typically requires minimal paperwork. Since there are no formal registration requirements, the startup costs are significantly lower compared to other business structures.
- Complete Control: Sole proprietors enjoy full autonomy over business decisions and operations. They have the freedom to implement their vision and make strategic choices without needing to consult with partners or shareholders.
- Simplified Taxation: From a tax perspective, sole proprietorships offer simplicity and convenience. Business income and expenses are reported on the proprietor’s personal tax return using Schedule C (or Schedule C-EZ), avoiding the need for separate corporate tax filings. This streamlines the tax process and reduces administrative burdens.
Disadvantages: Despite their simplicity, sole proprietorships also come with inherent drawbacks that entrepreneurs should consider:
- Unlimited Personal Liability: Perhaps the most significant disadvantage of a sole proprietorship is the lack of legal separation between the business and its owner. As a result, the proprietor bears full personal liability for any debts, obligations, or legal liabilities incurred by the business. In the event of lawsuits, creditor claims, or business losses, personal assets such as savings, investments, and real estate are at risk of seizure to satisfy business debts.
- Limited Growth Potential: Sole proprietorships may face challenges when it comes to scaling and expanding the business. The reliance on personal funds and resources can restrict access to capital, limiting growth opportunities. Additionally, the absence of a formal business structure may deter potential investors or lenders who prefer the security and structure offered by other entity types.
While sole proprietorships offer simplicity and flexibility, entrepreneurs must carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages to determine if this business structure aligns with their goals and risk tolerance. Seeking guidance from legal and financial professionals can provide valuable insights and help mitigate potential risks associated with unlimited personal liability.
By thoroughly understanding the implications of operating as a sole proprietor, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions to set themselves up for success in their business endeavors.
Interesting Fact: Sole proprietorships are the most common form of business entity in the United States, making up over 70% of all businesses.
Partnerships
Partnerships represent a collaborative business structure formed by two or more individuals who join forces to pursue a common business objective. Let’s delve deeper into the various aspects of forming and operating a partnership:
Process: Establishing a partnership typically involves the creation of a partnership agreement, a legal document that delineates the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of each partner. While partnerships do not mandate formal registration with the state, crafting a comprehensive partnership agreement is essential to clarify the terms of the partnership and mitigate potential conflicts or misunderstandings down the line.
This agreement should address critical aspects such as profit-sharing arrangements, decision-making authority, contributions of capital and resources, management responsibilities, dispute resolution mechanisms, and procedures for admitting new partners or dissolving the partnership.
Advantages: Partnerships offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for entrepreneurs seeking to collaborate and pool resources:
- Shared Management and Decision-Making: Partnerships allow for shared management and decision-making among the partners. Each partner brings their unique skills, expertise, and perspectives to the table, fostering collaboration and synergy in the decision-making process.
- Access to Additional Capital and Resources: By combining the financial resources, skills, and networks of multiple partners, partnerships can access a more extensive pool of capital and resources than sole proprietorships. This enhanced financial leverage enables partnerships to pursue larger-scale projects, investments, or business ventures that may be beyond the reach of individual entrepreneurs.
- Pass-Through Taxation: Partnerships enjoy pass-through taxation, meaning that business profits and losses «pass through» to the individual partners, who report their share of the partnership income or losses on their personal tax returns. This eliminates the issue of double taxation faced by corporations, where profits are taxed at both the corporate and individual levels.
Disadvantages: Despite their benefits, partnerships also present certain challenges and risks that partners should be aware of:
- Unlimited Personal Liability: Similar to sole proprietorships, partnerships expose partners to unlimited personal liability for the debts, obligations, and legal liabilities of the business. This means that each partner is personally liable for the actions and debts of the partnership, including liabilities arising from contracts, lawsuits, or business losses.
- Complexity of Management: Partnerships can be complex to manage, particularly as the number of partners increases. Decision-making may require consensus among the partners, leading to potential delays or conflicts if partners have divergent opinions or interests. Effective communication, collaboration, and a clear understanding of each partner’s roles and responsibilities are essential to mitigate management challenges and ensure the smooth operation of the partnership.
While partnerships offer opportunities for collaboration, shared risk, and access to resources, prospective partners must carefully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages before entering into a partnership agreement. Seeking guidance from legal and financial professionals can help partners navigate the complexities of partnership formation and establish a solid foundation for their business venture.
By fostering open communication, mutual trust, and a commitment to shared goals, partners can maximize the benefits of their partnership while effectively managing potential risks and challenges.
Interesting Fact: The earliest recorded partnership agreement dates back to 1157 in Florence, Italy, where partnerships were commonly used in banking and trading ventures.
Corporations
Corporations represent sophisticated legal entities that provide unique advantages and challenges for business owners. Let’s delve deeper into the various aspects of forming and operating a corporation:
Process: The formation of a corporation entails several essential steps, each designed to establish the legal framework and governance structure of the entity:
- Filing Articles of Incorporation: To form a corporation, founders must file articles of incorporation, also known as a corporate charter or certificate of incorporation, with the appropriate state authority. These articles outline key details about the corporation, such as its name, purpose, registered agent, business address, and the number and type of authorized shares of stock.
- Adopting Corporate Bylaws: Once the articles of incorporation are approved, the corporation must adopt corporate bylaws, which serve as the internal rules and regulations governing the corporation’s operations and management. Bylaws typically address matters such as shareholder rights, board of directors’ responsibilities, meeting procedures, voting rights, and corporate governance procedures.
- Appointing Directors and Holding Meetings: Corporations are required to appoint a board of directors responsible for overseeing the corporation’s affairs and making strategic decisions on behalf of shareholders. Additionally, corporations must hold regular shareholder meetings to conduct business, elect directors, approve major corporate actions, and provide updates on corporate performance.
Advantages: Corporations offer several key advantages that make them an attractive option for entrepreneurs seeking to establish a separate legal entity for their business ventures:
- Limited Liability Protection: One of the primary advantages of a corporation is the limited liability protection it provides to shareholders. Shareholders are generally not personally liable for the debts, obligations, or legal liabilities of the corporation, shielding their personal assets from business-related risks and liabilities.
- Capital Formation: Corporations have the ability to raise capital by issuing shares of stock to investors in exchange for equity ownership. This allows corporations to access a broader pool of capital than other business entities and facilitates investment in growth opportunities, expansion initiatives, and strategic acquisitions.
- Perpetual Existence: Corporations have perpetual existence, meaning that they continue to exist independent of changes in ownership or the death of shareholders. This provides stability and continuity for the corporation’s operations and ensures that business activities can continue uninterrupted over the long term.
Disadvantages: Despite their advantages, corporations also present certain challenges and drawbacks that business owners should consider:
- Double Taxation: One of the most significant disadvantages of a corporation is the issue of double taxation. Profits earned by the corporation are subject to corporate income tax at the corporate level. Additionally, when dividends are distributed to shareholders, they are taxed again as individual income. This results in a higher overall tax burden compared to other business entities that enjoy pass-through taxation.
- Regulatory Requirements: Corporations are subject to greater regulatory requirements and administrative burdens than other business entities. They must comply with state corporate laws, federal securities regulations, and other regulatory frameworks governing corporate governance, reporting, and disclosure. Failure to adhere to these requirements can result in penalties, fines, or legal liabilities.
- Administrative Complexity: Operating a corporation involves significant administrative complexity, including maintaining corporate records, holding regular meetings, and complying with reporting and disclosure obligations. Corporations must also adhere to formalities such as issuing stock certificates, maintaining a corporate seal, and recording meeting minutes, adding to the administrative burden and operational costs.
While corporations offer unique advantages such as limited liability protection, capital formation, and perpetual existence, entrepreneurs must carefully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages before choosing this business structure. Seeking guidance from legal and financial professionals can help business owners navigate the complexities of forming and operating a corporation and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
By understanding the implications of operating as a corporation, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and objectives.
Interesting Fact: The world’s oldest corporation still in operation is the Stora Kopparberg mining community in Sweden, founded in 1347.
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) stand as a versatile and popular business entity that blends the benefits of both partnerships and corporations. Let’s delve deeper into the various aspects of forming and operating an LLC:
Process: Forming an LLC involves several key steps aimed at establishing the legal structure and operational framework of the entity:
- Filing Articles of Organization: The process begins with filing articles of organization, also known as a certificate of formation, with the appropriate state agency. These articles provide essential details about the LLC, including its name, registered agent, business address, members, and management structure. Once approved, the LLC is officially recognized as a separate legal entity.
- Creating an Operating Agreement: While not always required by state law, creating an operating agreement is highly advisable for LLCs. This document outlines the rights, responsibilities, and operating procedures of the LLC and its members. The operating agreement covers critical aspects such as management structure, decision-making processes, profit-sharing arrangements, membership interests, capital contributions, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses: Depending on the nature of the business and its location, LLCs may need to obtain various permits, licenses, or registrations to operate legally. These requirements vary by industry, state, and local jurisdiction and may include business licenses, professional licenses, zoning permits, health permits, and tax registrations.
Advantages: LLCs offer several compelling advantages that make them an attractive option for entrepreneurs seeking limited liability protection and operational flexibility:
- Limited Liability Protection: One of the most significant advantages of an LLC is the limited liability protection it provides to its members. Members’ personal assets are generally shielded from business liabilities, meaning they are not personally liable for the debts, obligations, or legal claims of the LLC. This protects members’ personal wealth and assets from being at risk in the event of business-related lawsuits or financial losses.
- Flexibility in Management and Taxation: LLCs offer flexibility in both management structure and taxation. Unlike corporations, which are subject to rigid governance requirements, LLCs have the freedom to choose their management structure, whether member-managed or manager-managed, based on the preferences and needs of the members. Additionally, LLCs have the option to elect their tax treatment, allowing members to choose between pass-through taxation like a partnership or corporate taxation like a corporation, depending on their tax planning objectives.
Disadvantages: While LLCs offer many benefits, they also come with certain limitations and drawbacks that prospective members should consider:
- Self-Employment Taxes: One potential disadvantage of an LLC is that members may be subject to self-employment taxes on their share of the LLC’s income. Unlike corporations, which pay corporate income tax, LLCs pass their profits and losses through to their members, who report them on their individual tax returns. This can result in members being subject to self-employment taxes, which include both the employee and employer portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes.
- Fewer Formalities than Corporations: While LLCs offer greater flexibility than corporations in many respects, they also have fewer formalities and requirements. This can lead to potential issues with governance and decision-making, as the absence of formal rules and procedures may result in ambiguity or disputes among members. To mitigate these risks, it’s essential for LLCs to adopt a well-drafted operating agreement that clearly defines the rights, responsibilities, and expectations of all members.
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) offer a unique blend of limited liability protection, operational flexibility, and tax advantages for entrepreneurs and business owners.
By understanding the formation process, advantages, and disadvantages of LLCs, individuals can make informed decisions about whether this business structure aligns with their goals and objectives. Seeking guidance from legal and financial professionals can provide valuable insights and assistance in navigating the complexities of forming and operating an LLC, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations and minimizing potential risks.
Interesting Fact: The first Limited Liability Company (LLC) statute in the United States was enacted in Wyoming in 1977, leading to the widespread adoption of the LLC as a popular business entity structure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right business entity is a crucial decision that can have significant implications for liability, taxation, governance, and overall business success.
By understanding the process and legal considerations involved in forming different types of business entities, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and objectives. Whether opting for a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or LLC, consulting with legal and financial professionals can provide valuable guidance and ensure compliance with state laws and regulations.